Key Takeaways
- Some DCTs are fully virtual but many are hybrid, with some assessments handled digitally while others take place in-clinic
- 77% of biotech companies surveyed plan to run a hybrid DCT in the next year
- DCTs collect vast data sets which must be converted to actionable insights
- Choosing the correct data platform is key to DCT success

DCT Technology Partner Checklist
Decentralized Clinical Trials (DCTs), also known as Digital Clinical Trials, were being explored as a new paradigm before the global COVID-19 pandemic, but there is no doubt that the pandemic accelerated their adoption. Getting a handle on exactly how many DCTs are being executed is difficult as much of the data about the number of trials is coming from the Clinical Research Organizations that offer DCT-related services. It is clear, however, that the interest in the industry is extensive. A November 2021 survey reported by FierceBiotech found that 77% of respondents said they planned to run a hybrid DCT in the next 12 months compared to 59% for the previous year.1
What Is a Decentralized Clinical Trial?
DCTs can broadly be defined as those trials that employ digital technology to improve participant retention and recruitment, increase participant access and engagement, and collect some or all trial-related measurements outside a clinic setting. Two of the most common types of DCTs are:
- VIRTUAL CLINICAL TRIALS: A fully decentralized, or virtual, clinical trial has participant recruitment, consent, delivery/administration of study medication, and collection of outcome measurements all taking place without contact between participants and a clinical site
- HYBRID CLINICAL TRIALS: A hybrid model is one where some aspects of a trial (e.g., participant recruitment, consent, and electronic Clinical Outcome Assessments [eCOA]) are handled digitally, while other aspects (e.g., randomization, study medication distribution) are handled in-clinic
Decentralized Clinical Trials’ Vast Data Sets
Whether they are fully decentralized or hybrid, DCTs produce enormous amounts of data, particularly if they involve the collection of continuously monitored endpoints such as glucose levels or heart rate. If a DCT also collects Real World Data (RWD), the data sets will be even larger.
The FDA defines RWD as relating to patient health status and/or the delivery of health care routinely collected from a variety of sources, such as:
- Electronic Health Records (EHR)
- Patient-generated data including in home-use settings
- Data that can inform on health status such as from mobile devices2
Making Decentralized Clinical Trials Data Actionable
To control, understand, and make actionable the immense amounts of data collected in DCTs will involve the use of other digital technologies such as cloud-based data platforms and artificial intelligence (AI). Such technologies could play an important role in deriving useful information from digital endpoints gathered from DCTs. Examples:
- Complicated digital signals such as images that allow for the derivation of new clinical endpoints (e.g., diabetic retinopathy or cancerous skin lesions) have shown promise, reaching clinician-grade quality in multiple novel trials3
- Examining the images from 5,000 patients with hypertension to detect if there is a correlated biomarker in the eye
Why Are Data Privacy and Security Important for Decentralized Clinical Trials?
As with all medical research, data collected in DCTs must comply with rigorous security and regulatory standards, in a global setting. For example, data must be handled in compliance with:
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the U.S.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe
- Human Genetic Resources Administration of China (HGRAC)
To preserve participants’ privacy and promote the trust required for medical research, DCT infrastructure must achieve the confidence level of other sectors dealing with private and highly sensitive information digitally, such as finance and banking. The provision of a verifiable and tamper-proof history of all transactions offers greater assurance of data security.4
Secure, Cloud-Based, API Ready Data Platforms: Vital for DCT success
With the increasing prevalence of DCTs, pharmaceutical, biotech, and CRO companies will find great value in turning to clinical endpoint service providers who offer a robust, secure, and API-ready data platform. Such a data platform may be integrated tightly with a sponsor or institution’s data warehouse.
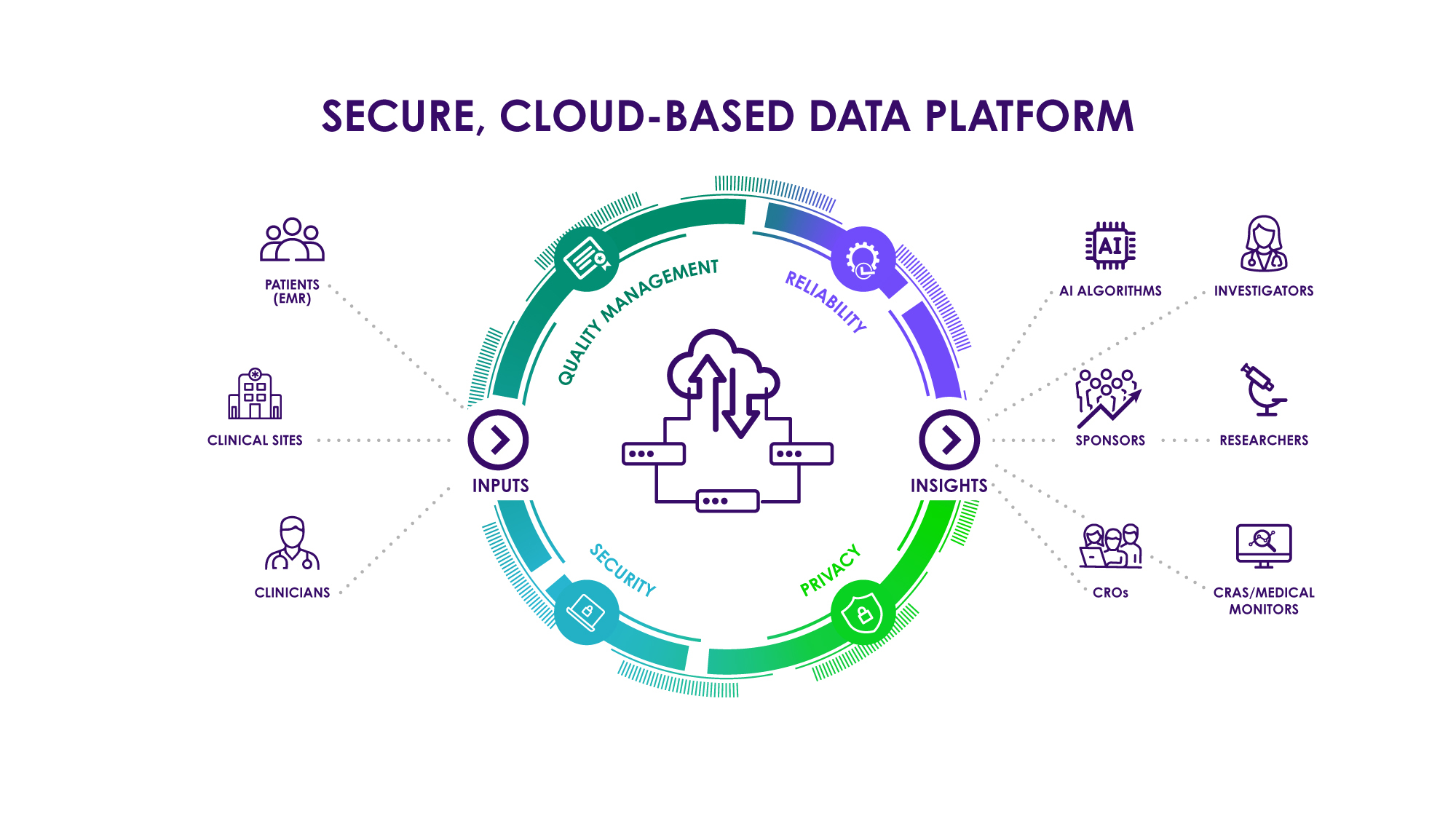 Example: Direct connection with Sponsor’s AI and machine learning systems. EHR systems also integrated through API. Data platform must be HIPAA, 21 CFR part 11, GDPR, and HGRAC compliant.
Example: Direct connection with Sponsor’s AI and machine learning systems. EHR systems also integrated through API. Data platform must be HIPAA, 21 CFR part 11, GDPR, and HGRAC compliant.
Turn DCT Data into Actionable Results WITH MERIT
MERIT’s suite of services and technology empowers sponsors to turn DCT data into actionable results. Our proprietary cloud-based software, EXCELSIOR™, offers the following differentiators:
- Effective and instantaneous transfer of data from one location to another. Image data can be directly and automatically moved to the sponsor’s data warehouse for further analysis, helping fuel the Sponsor’s AI system
- Access to the data in real-time
- No geographic limitations. With cloud-based data infrastructure, data can be viewed and analyzed anywhere
- Latest web and imaging technologies for data cleaning, standardization, analysis, reading, and reporting
- EXCELSIOR’s regulatory compliance includes HIPAA, 21 CFR part 11, GDPR, and HGRAC and is cleared with the FDA as a class II medical device in ophthalmic and radiology indications. MERIT’s Quality Management System is ISO 13485 certified

MERIT EXCELSIOR Software Solution Guide
References
1 LaHucik K. About 77% of clinical research execs expect to run decentralized trials in next 12 months: survey. Fierce Biotech website. Accessed 03Oct2022. fiercebiotech website
2 Real-world data (RWD) and real-word evidence (RWE) are playing an increasing role in health care decisions. FDA website, accessed 03Oct2022. FDA website
3 De Brouwer, W., Patel, C.J., Manrai, A.K. et al. Empowering clinical research in a decentralized world. npj Digit. Med. 4, 102 (2021). DOI website
4 Steinhubl, S.R., Wolff-Hughes, D.L., Nilsen, W. et al. Digital clinical trials: creating a vision for the future. npj Digit. Med. 2, 126 (2019). DOI website


